Revision Knee surgery (Re-do surgery on your knee) is carried out if your knee replacement is causing any problems.
Commonest reasons for revising the knee replacement include:
1. Aseptic loosening (wear and tear of the knee replacement with loosening)
2. Infection
3. Stiff knee
4. Unstable knee
5. Fracture around the knee joint
6. Problems with your knee cap
7. Persistent pain
The most common scenario is that your artificial knee has been functioning well for quite some time, but gradually starts giving you problems like discomfort, laxity, instability, pain, etc.
Occasionally, some patients may develop stiffness following knee replacement surgery. If this fails to improve my exercises and physiotherapy, further procedures can be considered.
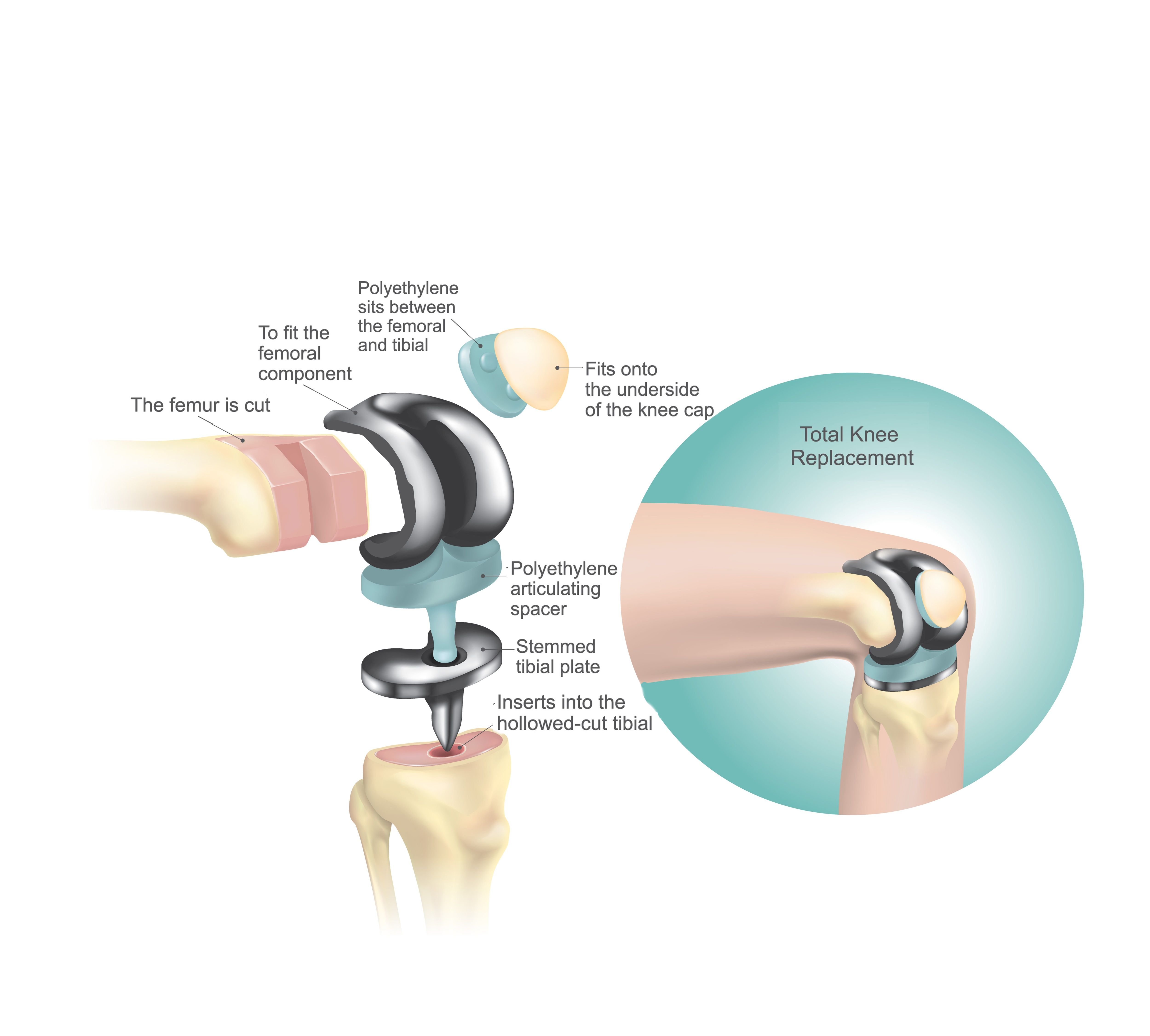
Revision knee surgery generally involves removing some or all of the old components of your knee replacement, followed by re-implantation of new implants.
Careful pre-operative planning is performed in each individual case and the type of new knee replacement is determined accordingly.
Overall, revision knee replacement is a reasonably successful operation in modern-day surgery. In my practice, the success rate of a revision knee replacement is 85% or higher. This does vary on a case-by-case basis and I will be happy to discuss this with you during the consultation.
Risks of revision knee surgery are similar to that of total knee replacement but are deemed to be slightly higher. These include infection (around 2-3%), bleeding, DVT (clots in your leg), PE (clots in your lung), stiffness, loosening, wear, persistent pain (around 1%), medical and anesthetic complications. Precautions are taken in order to minimize all the above risks e.g. use of antibiotic prophylaxis and specialized laminar airflow theatres to minimize the risk of infection, use of blood-thinning medications, and mechanical methods to reduce the risk of clots, etc. Post-operative exercises are extremely important to decrease the risk of post-operative stiffness.
You are generally admitted to the hospital on the day of surgery. The average length of stay in the hospital is 3-4 days. During the hospital stay, a multi-disciplinary team including an orthopaedic team, ward doctor, nursing staff, physiotherapist, and occupational therapist, treats you. Once you and the team are happy with the progress, you are discharged from the hospital.
Post-operative mobilization includes the use of walking aids like walkers or crutches, to begin with. You can subsequently use the walking stick/s until independent mobility can be achieved.
You can expect some swelling and redness around the wound and of the lower leg for a few weeks. Generally, by 12 weeks, functional recovery can be expected in most patients. Most patients can expect to drive around 6 to 8 weeks mark.
Copyright by FUW 2017-2026. All rights reserved.